ASHALATHA IVF CENTRE
Reddy & Reddy Colony
Tirupati-517501
Ph: 09949900097::09949542399::08772228240
E-mail: ashalathaivf@gmail.com
Error message
- Warning: include(/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
- Warning: include(): Failed opening '/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/pear:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/php') in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
Infertility
Ashalatha IVF Centre is one of the perfect IVF Centers in India in the assessment and treatment of couple with fertility problems both male and female.
Introduction
Fertility problems affect one in ten couples in India. Most couples (about 84 out of every 100) who have regular sexual intercourse (that is, every 2 to 3 days) and who do not use contraception will get pregnant within a year. Women become less fertile as they get older.
If women are not able to get pregnant even after 2 years of regular unprotected sexual intercourse, either one, or both, of the couple may have a fertility problems.
 |
 |
Causes of Infertility
In men, a fertility problem is usually because of low number or poor quality of sperms. A woman may have fertility problems because she does not produce eggs regularly or because her fallopian tubes are damaged or blocked and the sperms cannot reach the eggs.
For nearly one third of people, no reason can be found for their problem. This is known by healthcare professionals as having unexplained fertility problems.
General advice for couple
There are certain things couple can follow to improve their chances of coception.
How often to have sexual intercourse
For the best chance of success, couple need to have sexual intercourse every 2 to 3 days throughout the month. Maximum fertile period is variable. In women with 26-30days menstrual cycle the maximum fertile days begin on day 9 to day 17.
Alcohol
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can affect the quality of a man’s sperm.
Smoking
Smoking causes poorer quality of sperm, .
Body weight
The range of healthy weight is defined by a measurement known as the body mass index (BMI). BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in metres squared (that is, your height in metres multiplied by itself). A healthy weight is one that gives a BMI of between 20 and 25.
Women who are overweight (BMI of more than 29) and who have irregular periods, or no periods at all, loosing weight may increase chances of getting pregnant.
Tight underwear for men
wearing tight-fitting underwear raises the temperature in the testicles and could reduce the quality of a man's sperm.
Your work
Certain types of work conditions expose people to the chemicals like tar, pesticide, to high temperature like those working in furnace etc can reduce sperm quality
Folic acid
Women who are trying to get pregnant should usually take folic acid tablet, it reduces the chances of spina bifida and other neural tube defects in the baby.
German measles (rubella)
Women are offered blood test IgG for Rubella. The test results will reveal whether person has acquired the infection in past. Those who are not immune to rubella can be offered vaccination. Women should not become pregnant for at least 3 months after vaccination.
Consultation for Fertility problems
It is advisable that both husband and wife should be present on the first day of consultation. Information provided by the couple and the test results remain confidential.
Doctor will take your detailed information regarding menstrual details, married life,past history of any medical or surgical diseases. Men are usually referred to andrologist in the centre for checkup.
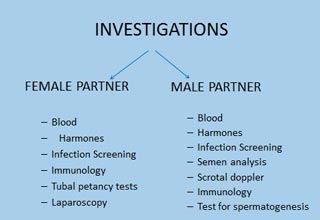
Investigating for fertility problems
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
Initial assessment – Blood tests like hemogram,blood sugar, blood urea, S.creatinine, Viral screening, VDRL, Thyroid function test, Complete abdomen and pelvic scan are done for female partner & Semen analysis, viral screening, Thyroid profile for male partner.
Checking hormone levels
Day2/Day3 fasting blood test are done for FSH, LH, E2, T3, T4, TSH and Prolactin (day2 is 2nd day of menstrual flow)
Day21 progestrone blood test is done for confirmation of ovulatory cycles
AMH (Antimullarian hormon) estimation is done for women in whom low ovarian reserve is suspected
Checking for fallopian tubes and ruling out uterine malformations
Hysterosalpingo-graphy is done to check the patency of tubes. It is an out patient procedure and done in a X-ray unit. A cannula is placed in the cervical canal and dye is slowly pushed and X-ray is taken while doctor pushes the dye. Film is developed and viewed for uterine cavity contour and tubal patency.
Treatment for male
Male infertility may be caused by
- Hormone disorder
- Blockage in testicles
- Low sperm count (known as oligozoospermia)
- Poor sperm quality or unable to ejaculate.
- Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism
gonadotropin hormones (which stimulate the production of sperm) are given to men who have low hormone levels(FSH, LH) - If the flow of sperms from the testicles is blocked surgery can be offered to remove the blockage. Other alternatives include surgical sperm recovery or in vitro fertilisation.
- unable to ejaculate
Treatments with certain medication can restore ability and improve the fertility. The other alternatives are surgical sperm recovery or assisted reproduction procedures. - If sperm count is found to be abnormal, treatment varies with the severity.
- Mildly abnormal – up to six cycles of intrauterine insemination (IUI) can be offered.
- Moderately abnormal – success rates are more with IVF/ICSI treatment.
- Severely abnormal- intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) which involves injection of sperm directly into egg improves the chances of coception.
Treatment for female
Infertility may be
- Because of not ovulating normally.
- Because of blockage in fallopian tubes.
Treatment for anovulation
In a natural cycle a woman should produce one egg. If women is suffering from ovulatory disorder, ovaries can be stimulated with medications to produce eggs (this is known as ovulation induction). The type of treatment will depend on the cause of anovulation.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a condition where ovaries produce more small follicles (the sacs in which eggs develop) than normal but fail to ovulate regularly. In women with PCOS, the first treatment is drug treatment with either clomifene citrate or tamoxifen. If ovulation is documented this treatment can extended up to maximum of 6 months. There is an increased risk of having twins, with this treatment (known as multiple pregnancy).
Clomiphene treatment is not successful in all cases of PCO. Women who ovulate but do not get pregnant should be offered IUI along with ovulation induction.Those who do not ovulate with Clomiphene and are obese (BMI>25) should be given Metformin along withCC.
Alternatively, clomifene citrate failures should be offered
- Laparoscopic ovarian drilling.
- Gonadotrophin hormone treatment.
Laparoscopy involves a surgical procedure that requires anaesthesia.
Gonadotrophin hormone treatment.
Gonadotrophins (follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH], human menopausal gonadotrophin (HMG), GNRH agonists and antagonists are used to induce ovulation which improves the chances of pregnancy.
Other ovulation disorders
Women with ovulation disorders caused by low levels of gonadotrophin hormones and low oestrogen, can be treated wth pulsatile gonadotrophin-releasing hormone or gonadotrophins.
Women with Hyperprolactinaemia (a disorder of the pituitary gland which can cause irregular periods, production of breast milk and fertility problems) can be treated with drugs such as bromocriptine, and cabergolin.
Women with blocked fallopian tubes
- Should be offered IN VITRO FERTILISATION
- Tubal surgery
If the blockage in fallopian tubes is close to uterus, a procedure called ‘selective salpingography with tubal catheterisation or cannulation’ can improve chances of conception.
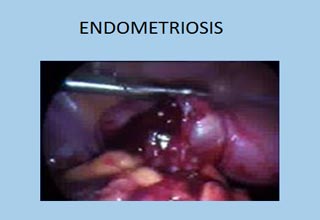
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where cells similar to the inner lining of the uterus (Endometrium) are found in other areas of the pelvis. Endometriosis can cause pain and damage to uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
It can be mild, moderate or severe and treatment is mandatory at the earliest by laparoscopy procedure known as surgical ablation or resection to remove or destroy the endometriotic spots and release of adhesions. This can improve chances of conception.
Following surgical removal of endometriosis if tubal patency is good, ovulation induction and intrauterine insemination (IUI) up to six cycles can be tried before proceeding to IVF.
Uterine synechiae
Some women who have scanty menstrual flow and HSG shows irregular cavity with filling defects which raises suspicion of intrauterine bands/adhesions, can be confirmed and treated with procedure called Hysteroscopy with an instrument called hysteroscope that is inserted into the uterus. This enables the surgeon to see and clear the adhesions.
Treatment for unexplained fertility problems
In case of unexplained infertility following treatments can be offered
- Clomifene citrate to stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs
- Assisted reproduction techniques through
Intrauterine insemination
In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
ICSI
Assisted reproduction
Assisted conception broadly refers to procedures whereby treated or manipulated sperms are brought into proximity with oocytes. It includes:
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI) with husband or donor sperms (in natural or stimulated cycles)
- In vitro fertilisation and embryo transfer (IVF-ET)
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
- The use of donor sperms (donor insemination) or eggs (egg donation).
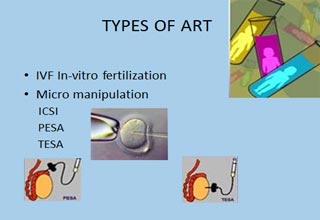
 IVF, ICSI, IUI IVF, ICSI, IUI Assisted Reproduction |
 Laproscopic Surgeries Laproscopic Surgeries Hystero Scopy |
|
Mammography & Breast Care |
Copyright © 2026 ashalathaivf.com. All Rights Reserved.
Site Developed by SRI WEBSITE DESIGN & DEVELOPMENT
