ASHALATHA IVF CENTRE
Reddy & Reddy Colony
Tirupati-517501
Ph: 09949900097::09949542399::08772228240
E-mail: ashalathaivf@gmail.com
Error message
- Warning: include(/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
- Warning: include(): Failed opening '/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/pear:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/php') in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
Laparoscopy
What is laparoscopy?
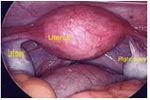
This is a type of operation where a fine telescope (laparoscope) is introduced through a small cut (key hole) in umbilicus (belly button) to look into the pelvis (Lower tummy) & abdomen.
Why is a laparoscopy performed? Laparoscopy involves direct visualization of inside organs. It can be offered to confirm the diagnosis in patients, who complain of pelvic pain, causes of infertility, to diagnose endometriosis, to ascertain the extent of adhesions, to see the pelvic mass etc..
How is laparoscopy performed?
The patient is admitted to the hospital usually for a day. The operation is done preferably under general anaesthesia. A small cut is made on the tummy button; carbon dioxide gas (a harmless gas) is introduced into the tummy through a metal pipe called port. The telescope with camera is then inserted to look inside theabdomen& pelvis and view the contents. Depending on the indication for laparoscopy, further small cuts may be made around the lower tummy to allow other instruments to be introduced into the pelvis to complete the operation. The operation will last about 15 to 30 minutes usually, after which the gas is let out of the tummy, and dissolvable stitches are placed on the cuts .If there are no complications and patient if comfortable, she is discharged next day.
There are many laparoscopic procedures.Lap is usefull in many abdominal operations How Minimally Invasive Procedures Work? When to do.
Laparoscopy in Gynaecology
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
||
 |
 |
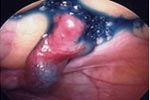 |
To diagnose Ovarian causes of Infertility
 |
 |
To diagnose causes for chronic pelvic pain

Laparoascopy to diagnose uterine anomalies

Laparoscopy in torsion of viscus

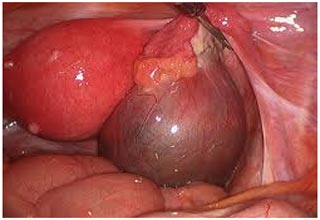
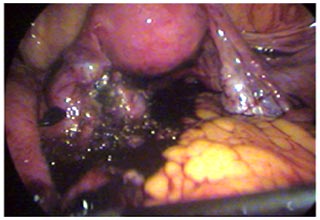
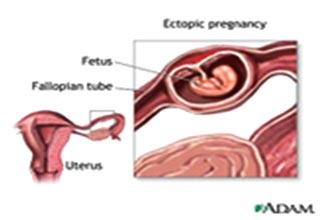
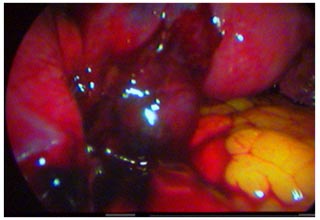
Laparoscopy in Ectopic pregnancy

What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that has implanted outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes but sometimes in the cervix or elsewhere in the abdominal region.
Statistics on Ectopic Pregnancy:
Statistics vary, but most estimates suggest that ectopic pregnancies happen in 1 out of every 40 to 100 pregnancies.
Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy:
Ectopic pregnancy may cause cramping on one or both sides of the lower abdominal area, along with normal pregnancy symptoms such as breast tenderness, missed period, etc. Some women will have vaginal bleeding or spotting, and hCG levels may rise more slowly than expected.
An ectopic pregnancy that has ruptured will cause severe pain in the abdominal area and possibly dizziness or fainting. Some women also have shoulder pain.
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancies:
Sometimes doctors detect an ectopic pregnancy that is not at risk of rupturing. The doctor may prescribe a medication called methotrexate, which should cause the ectopic pregnancy to miscarry. The woman would also be closely monitored until the hCG levels return to zero in order to be sure that the miscarriage is complete.
If an ectopic pregnancy is at risk of rupturing or has already ruptured fallopian tube, the treatment is laparoscopic surgery, because this situation is life threatening. Sometimes doctors must remove the fallopian tube
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
Tubectoy—family planning operation in females
Laparoscopic tubectomy in India is an effective, reliable, safest and permanent method for contraception. It is a common choice for women as Laparoscopic tubectomy is simple, has fewer complications with shorter hospital stay.
 |
 |
|
 |
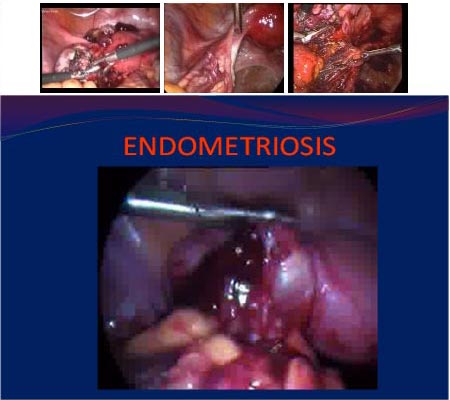
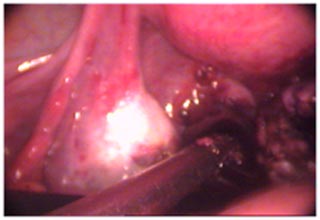
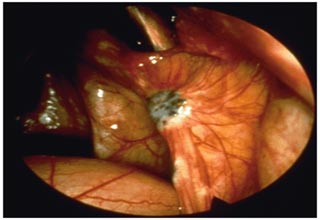
Laparoscopy in Endometriosis
Laparoscopy is the most common procedure used to diagnose and remove mild to moderate endometriosis. Instead of using a large abdominal incision, the surgeon inserts a lighted viewing instrument called a laparoscope through a small incision. If the surgeon needs better access, he or she makes one or two more small incisions for inserting other surgical instruments.
 |
||
 |
||
 |
 |
|
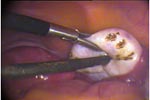
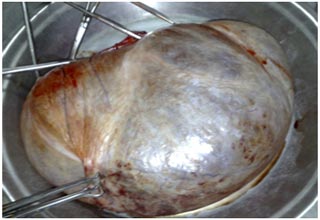
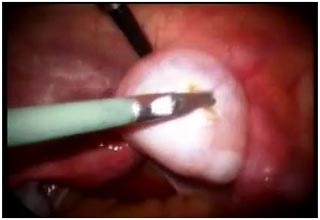
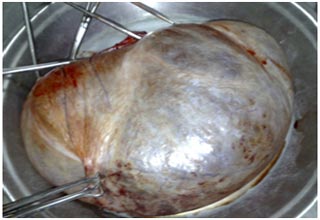
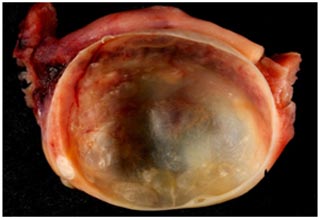
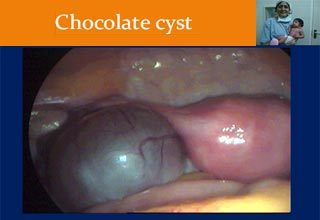
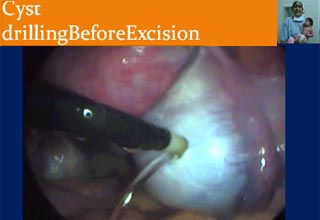
Laparoscopic Management of Ovarian cysts
An ovarian cyst is collection of fluid, surrounded by a very thin wall, within an ovary. Any ovarian follicle that is larger than two centimeters is termed an ovarian cyst. Such cysts range in size from as small as a pea to larger than an orange. Most ovariancysts are functional in nature and harmless (benign). Ovarian cysts affect women of all ages. They occur most often, however, during a woman's childbearing years. Some ovarian cysts cause problems, such as bleeding and pain. Surgery may be required to remove cysts larger than 5 centimeters in diameter.
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
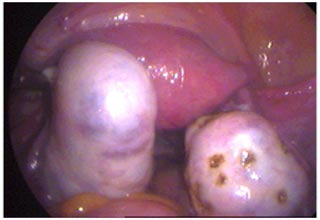
POLYCYSTIC OVARIES
Laparoscopic myomectomy
Myomectomy, sometimes also called fibroidectomy, refers to the surgical removal of uterine leiomyomas, also known as fibroids. In contrast to a hysterectomy the uterus remains preserved and the woman retains her reproductive potential. The presence of a fibroid does not mean that it needs to be removed. Removal is necessary when the fibroid causes pain or pressure, abnormal bleeding, or interferes with reproduction. The fibroids needed to be removed are typically large in size, or growing at certain locations such as bulging into the endometrial cavity causing significant obliteration of cavity.
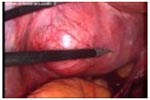 |
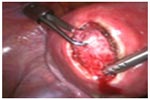 |
Laparoscopic adhesiolysis
Adhesions are bands of scar tissue that form between organs. In the abdomen, they form after an abdominal surgery or after any intra-abdominal infection (ie, pelvic inflammatory disease, diverticulitis). Although most adhesions are asymptomatic, some can cause bowel obstruction, infertility, and chronic pain requiring adhesiolysis to relieve the bowel obstruction. If the surgeon encounters adhesions, they can be easily divided using long laparoscopic instruments. The procedure is called adhesiolysis. A patient recovers quickly after laparoscopic surgery for adhesions as he / she has very little pain.
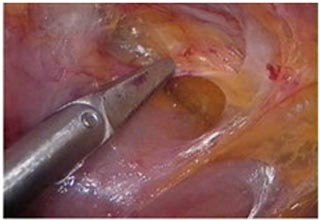 |
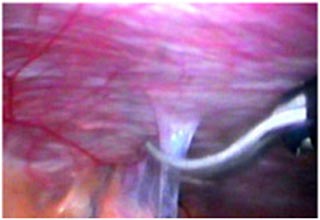 |
Laparoscopic hysterectomy
Vaginal and laparoscopic hysterectomies have been clearly associated with decreased blood loss, shorter hospital stay, speedier return to normal activities, and fewer abdominal wall infections when compared with abdominal hysterectomies. In light of these findings, a recent review concluded that vaginal hysterectomy is preferable to abdominal hysterectomy and that a laparoscopic hysterectomy should be attempted when vaginal hysterectomy is not possible. The vaginal approach is less expensive, but may be challenging in patients with a history of an adnexal mass, endometriosis, pelvic pain, and prior abdominal surgery, or in patients with a narrow pubic arch or poor vaginal descent. 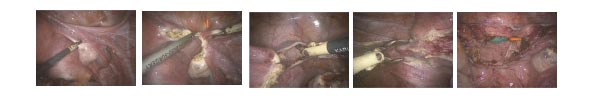
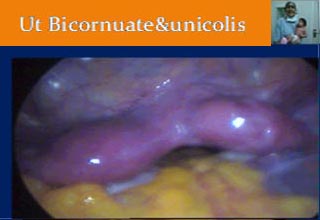
Laparoscopy in the diagnosis of congenital abnormalities
Uterus bicornuate
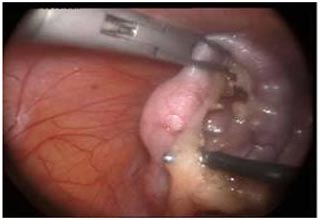
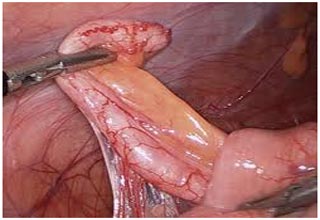
Laparoscopy in general surgery
Appendectomy (sometimes called appendicectomy) is the surgical removal of the vermiform appendix. This procedure is normally performed as an emergency procedure, when the patient is suffering from acute appendicitis or elective planned appendicectomy in chronic appendicitis.
 |
 |
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy( removal of gallbladder)
Cholecystectomy is one of the most commonly performed abdominal surgical procedures, and in developed countries many are performed laparoscopically. As an example, 90 percent of cholecystectomies are performed laparoscopically . Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is considered the "gold standard" for the surgical treatment of gallstone disease. This procedure results in less postoperative pain, better cosmesis, shorter hospital stays and less disability from work than open cholecystectomy 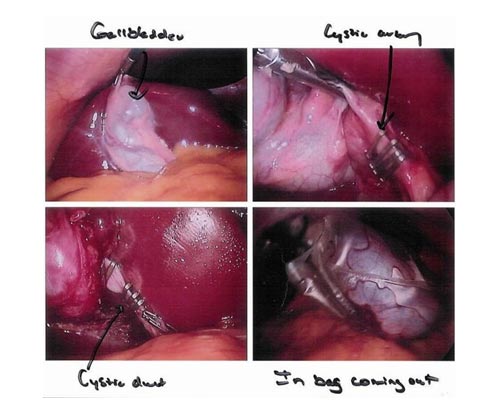
Benefits
Key hole surgery offers many benefits like short hospital stay, less blood loss, less post operative pain, early recovery &early to work, No incision- related complications like wound infections or hernias
What are the instructions given to the patient before laparoscopy?
Patients are first evaluated for the fitness for surgery and anaesthesia after necessary blood tests ,cardiac evaluation,scan etc are done.patient is instructed to come on the day of surgery on fasting along with attendant and records.
What happens after the operation?
Patients are usually monitored in ward. Necessary medication like antibiotics, pain killers,IV fluids are given.patient is usually allowed to take orally after 6-8 hrs of the surgery
Laparoscopy is quite usefull as diagnostic tool and also serves for therauptic purposes. Laparoscopy is the diagnostic tool for endometriosis and to remove adhesions, to remove endometriotic spots, to remove lesions like tumors, cysts etc...
 IVF, ICSI, IUI IVF, ICSI, IUI Assisted Reproduction |
 Laproscopic Surgeries Laproscopic Surgeries Hystero Scopy |
|
Mammography & Breast Care |
Copyright © 2026 ashalathaivf.com. All Rights Reserved.
Site Developed by SRI WEBSITE DESIGN & DEVELOPMENT
