ASHALATHA IVF CENTRE
Reddy & Reddy Colony
Tirupati-517501
Ph: 09949900097::09949542399::08772228240
E-mail: ashalathaivf@gmail.com
Error message
- Warning: include(/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
- Warning: include(): Failed opening '/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/pear:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/php') in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
Obstetrics
Obstetrics (from the Latin obstare, "to stand by") is the medical specialty dealing with the care of all women's reproductive tracts and their children during pregnancy (prenatal period), childbirth and the postnatal period. Many obstetricians are also gynecologists, meaning they perform in both specialties.
Ours is a 100 bedded hospital, with a fully equipped labor ward and operation theater, latest high end USG machine, CTG machine. Our Unit offers 24 hrs emergency obstetric care for safe delivery for normal and high risk cases. All essential facilities like continuous fetal cardiac monitoring, Labor analgesia (pain free delivery) are available round the clock. After delivery babies are managed by experienced Neonatologist.
- High risk pregnancy – Pregnancies in elderly women, women with bad obstetric history, Pregnancy induced hypertension, Gestational DM, multiple pregnancy, Women with medical diseases like asthma, NIDDM, thyroid disorder.
- Miscarriage clinic: Unit offers treatment for Women with history of repeated pregnancy losses. Blood tests including karyotyping are available to investigate the cause of RPL.
- Antenatal clinic: Offers essential obstetric care to normal low risk cases. All facilities of routine blood tests, triple test for anuploidy.
- Nuchal Translucency scan, Targeted Imaging For Fetal Anomaly, Fetal Echo, Fetal Doppler, Biophysical profile, Non Stress Test for fetal wellbeing
- Post natal Clinic –Offers postpartum checkup and contraceptive advise and post natal exercises.
- Early pregnancy unit: Offers care to women presenting with complaints of pain abdomen, bleeding per vaginum in first trimester of pregnancy.
- Family planing unit: All contraceptives are available, couple is provided with the counselling regarding various methods after delivery.
- IUCD insertion and laparoscopic tubal ligation are available in the hospital.
Management protocol
First trimester
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood type
- General antibody screen (indirect Coombs test) for Hemolytic disease of newborn.
- Rh D negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGam at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease.
- Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) to screen for syphilis
- Rubella antibody screen
- Hepatitis B surface antigen
- Gonorrhea and Chlamydia culture
- PPD for tuberculosis
- Pap smear
- Urinalysis and culture
- HIV screen
- Group B Streptococcus screen – will receive IV penicillin or ampicillin (it is much cheaper and has a wider coverage) if positive (if mother is allergic, alternative therapies include IV clindamycin).
Genetic screening for Downs syndrome (trisomy 21) and trisomy 18 is rapidly evolving away from the AFP-Quad screen for downs syndrome- done typically in the second trimester at 16–18 weeks. The newer integrated screen (formerly called F.A.S.T.E.R for First And Second Trimester Early Results) can be done at 10 plus weeks to 13 plus weeks with an ultrasound of the fetal neck (thick skin is bad) and two chemicals (analytes) Papp-a and bhcg (pregnancy hormone level itself). It gives an accurate risk profile very early. There is a second blood screen at 15 to 20 weeks which refines the risk more accurately. The cost is higher than an "AFP-quad" screen due to the ultrasound and second blood test but it is quoted to have a 93% pick up rate as opposed to 88% for the standard AFP/QS.
Second trimester
- MSAFP/quad. screen (four simultaneous blood tests) (maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein; inhibin; estriol; bhcg or free bhcg) - elevations, low numbers or odd patterns correlate with neural tube defect risk and increased risks of trisomy 18 or trisomy 21
- Ultrasound either abdominal or trannsvaginal to assess cervix, placenta, fluid and baby
- Amniocentesis is the national standard for women over 35 or who reach 35 by mid pregnancy or who are at increased risk by family history or prior birth history.
Third trimester
- Hematocrit (if low, mother will receive iron supplementation)
- Glucose loading test (GLT) - screens for gestational diabetes; if > 140 mg/dL, a glucose tolerance test (GTT) is administered; a fasting glucose > 105 mg/dL suggests gestational diabetes.
Most doctors do a sugar load in a drink form of 50 grams of glucose in water and draw blood an hour later (plus or minus 5 minutes) ; If glucose levels are more than 145mg/dl then GTT is advised.
Imaging
A normal gestation would reveal a gestational sac, yolk sac, and fetal pole. The gestational age can be assessed by evaluating the mean gestational sac diameter (MGD) before week 6, and the crown-rump length after week 6. Multiple gestation is evaluated by the number of placentae and amniotic sacs present.
Fetal assessments
Obstetric ultrasonography is routinely used for dating the gestational age of a pregnancy from the size of the gestational sac, crown rump length of embryo & presence of fetal cardiac activity is the most accurate dating being in first trimester before the growth has been significantly influenced by other factors. Ultrasound is also used for detecting congenital anomalies (or other fetal anomalies) by TIFFA SCAN WITH FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY and determining the biophysical profiles (BPP), which are generally easier to detect in the second trimester when the fetal structures are larger and more developed. Specialised ultrasound equipment can also evaluate the blood flow velocity in the umbilical cord, looking to detect a decrease/absence/reversal or diastolic blood flow in the umbilical artery i.e. FETAL DOPPLER STUDY.
 |
 |
|
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
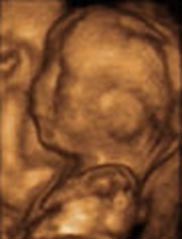
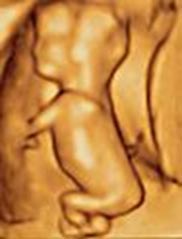
| Fetus sucking its thumb | 20wks fetus | u/s image of fetus (related pics) |
Labor
Childbirth - During labor the obstetrician is called on to do a number of tasks. These tasks include:
- Monitor the progress of labor, by reviewing the nursing chart, performing vaginal examination, and assessing the trace produced by a fetal monitoring device (the cardiotocograph)

- Accelerate the progress of labor by infusion of the hormone oxytocin
- Provide pain relief, either by nitrous oxide, opiates, or by epidural anesthesia done by anaesthestists, an anesthesiologist,.
- Surgically assisting labor, by forceps or the Ventouse (a suction cap applied to the fetus' head)
- Caesarean section, if there is an associated risk with vaginal delivery, as such fetal or maternal compromise supported by evidence and literature. Caesarean section can either be elective, that is, arranged before labor, or decided during labor as an alternative to hours of waiting. True "emergency" Cesarean sections include abruptio placenta, and are more common in multigravid patients, or patients attempting a Vaginal Birth After Caeserean section (VBAC)
Postnatal care is care provided to the mother following parturition.
Postnatal care
A woman who is delivering in a hospital may leave the hospital as soon as she is medically stable and chooses to leave, which can be as early as few hours postpartum, though the average for spontaneous vaginal delivery (SVD) is 1–2 days, and the average caesarean section postnatal stay is 3–4 days.
During this time the mother is monitored for bleeding, bowel and bladder function. The infant's health is also monitored.
Certain things must be kept in mind as the physician proceeds with the post-natal care.
- General Condition of the patient.
- Check for Vital Signs (Pulse, Blood Pressure, Temperature, Respiratory Rate)
- Palor
- Edema
- Dehydration
- Per Abdominal Examination (Fundus height following parturition, and the feel of the fundus)
- If an Episiotomy or a C-Section was performed, check the dressing for Oozing, haematomas, any signs of infection.
- Lochia (colour, amount, odour).
 IVF, ICSI, IUI IVF, ICSI, IUI Assisted Reproduction |
 Laproscopic Surgeries Laproscopic Surgeries Hystero Scopy |
|
Mammography & Breast Care |
Copyright © 2026 ashalathaivf.com. All Rights Reserved.
Site Developed by SRI WEBSITE DESIGN & DEVELOPMENT
