ASHALATHA IVF CENTRE
Reddy & Reddy Colony
Tirupati-517501
Ph: 09949900097::09949542399::08772228240
E-mail: ashalathaivf@gmail.com
Error message
- Warning: include(/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
- Warning: include(): Failed opening '/home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/sites/all/modules/views/theme/views-view.tpl.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/pear:/opt/alt/php56/usr/share/php') in theme_render_template() (line 1505 of /home/kbb5owh4p7zq/public_html/includes/theme.inc).
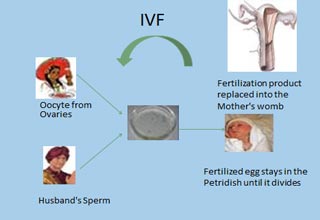
In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
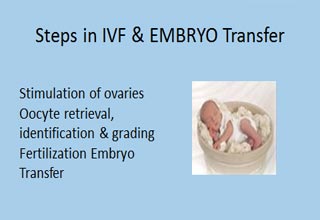
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is one of the main methods of assisted reproduction. It achieves pregnancy by fertilising woman's oocytes (eggs) out side her body. It involves:
- step 1: 'switching off' the woman's natural cycle of egg production in the ovaries (downregulation)
- step 2: stimulating the ovaries to produce more than one egg (ovulation induction)
- step 3: collecting the mature eggs from ovaries (retrieval of oocytes) and Incubated.
- step 4: collecting sperm from the man. Semen wash with highly sterile IVF medias and then kept in Incubator for 2 hours
- step 5: mixing the eggs and sperm and kept in Incubator
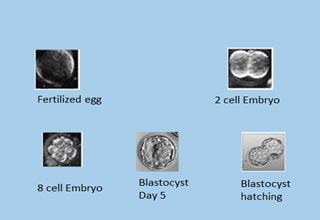
- step 6: Ferilisation check is done on the next day as 2 PN stage ; 2nd day - 2 to 4 cell embryo; 3rd day - 6 to 8 cell embryo
- step 7: Embryo transfer - 3rd day as 6 to 8 cell Embryo; 5th day as Blastocyst Transfer. Putting one or two or three embryos into the woman’s womb on Day3, Day5.
If an embryo successfully gets attached inside the womb and continues to grow, the result is a Pregnancy.
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
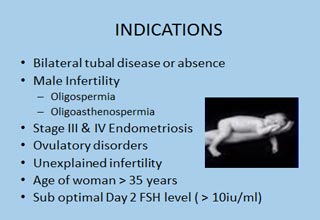
Factors affecting success of IVF
Success of having a baby through IVF varies depending on women’s age. The older a woman is, the less likely she gets pregnant. The best chance of success with IVF is in women between 23 and 39 years. IVF is more effective for women who have been pregnant or had a baby before(secondary infertility). Women have a better chance of success if they have a normal body weight (body mass index between 19 and 30). Obesity decreases the chances of fertility.
Downregulation of the ovaries (step 1)
Drugs known as gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonists are used in the form of nasal spray or an injection to 'switch off' egg production in the ovaries. They make the ovaries more responsive to the gonadotrophin hormones, which stimulate the ovaries to produce good eggs.
Ovulation induction (step 2)
Ovaries are stimulated using fertility drugs like FSH and HMG to produce more than one egg at a time.
The dose and duration vary from patient to patient. On an average 8-10 days are required to attain optimum size of the follicles. Serial ultrasound scans are done to monitor the size of follicles.
Egg collection (Ovum pickup) (step 3) - eggs will be collected using a special aspiration needle, through the vagina guided by ultrasound (known as ultrasound-guided aspiration). It is done under short general anesthesia.
Obtaining sperm (step 4)
On the same day of egg collection the male partner is asked to collect semen sample.
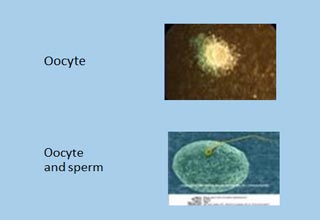
Fertilisation of the eggs (step 5)
Once eggs and sperms are collected, they are mixed together in a dish by droplet method under oil seal and placed in incubator. The eggs are fertilised by sperms. Resulting embryos are kept in the incubator for 3/5 days.
Transfer of the embryos (steps 6 and 7)
Grade 1 embryos are selected and transfered into uterus using a special embryo transfer catheter under ultrasound guidance. To balance the chances of a successful birth against the risk of having more than one baby, usually two to three grade I embryos are transferred.
Luteal support (step8)
Progestrone is given to help the successful implantation and continuation of pregnancy
Assisted hatching is a method used for refractory cases to thin or open the shell of an embryo in the early stages of development, which improves the chances of implantation.
 IVF, ICSI, IUI IVF, ICSI, IUI Assisted Reproduction |
 Laproscopic Surgeries Laproscopic Surgeries Hystero Scopy |
|
Mammography & Breast Care |
Copyright © 2026 ashalathaivf.com. All Rights Reserved.
Site Developed by SRI WEBSITE DESIGN & DEVELOPMENT
